pressure
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
INSPIRE themes
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
Resolution
-
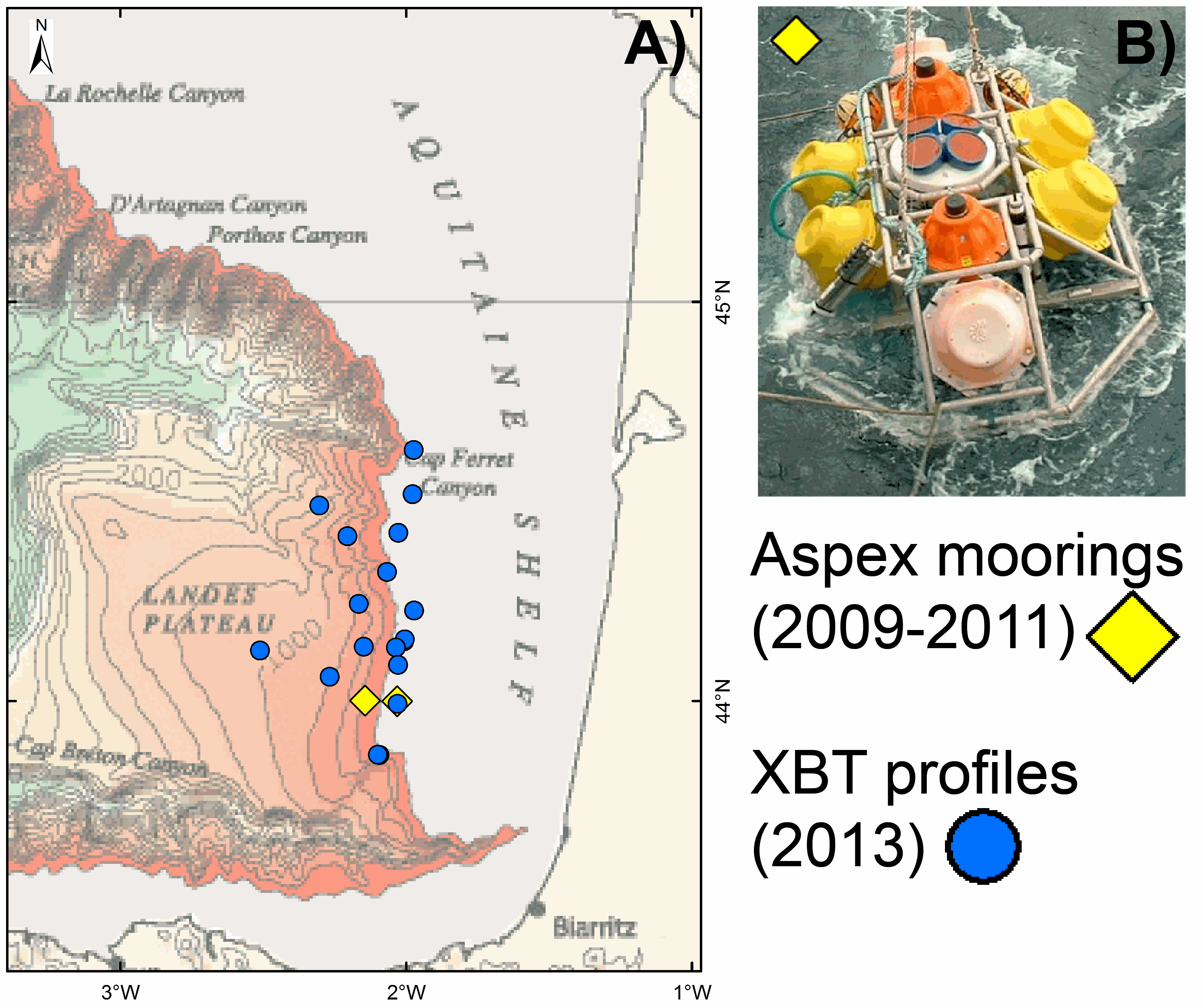
As part of the EPIGRAM project, two moorings, Aspex 9 and 10, equipped with temperature, conductivity and pressure sensors (Seabird microcat 37SM), were deployed offshore Aquitaine for a period of 2 years (2009-2011). The probes were calibrated in metrology and provide salinity values derived from calculations based on Fofonoff and Millard (1983) [Fofonoff, P. and Millard, R.C. Jr UNESCO 1983. Algorithms for computation of fundamental properties of seawater. UNESCO Tech. Pap. in Mar. Sci., No. 44, 53 pp. Eqn.(31) p.39. http://unesdoc.UNESCO.org/images/0005/000598/059832eb.pdf]. Several oceanographic missions ASPEX1, 2, 3 and 4, were dedicated to deploying and recovering these instruments. The frame of the mooring (Figure B) is laid on the seafloor with sensors at 0.5 m above it. Aspex 9 and 10 moorings are located at the continental shelf (at 148 m water depth) and continental slope (at 472 m water depth), respectively (Fig. A). Aspex 9 mooring recorded data from 18.07.2009 at 23:40:00 to 01.07.2010 at 09:18:00 (with a measurement every 120 seconds) and from 04.09.2010 at 23:30:00 to 10.08.2011 at 06:57:00 (with a measurement every 180 seconds). Aspex 10 mooring recorded data from the 18.07.2009 at 21:40:00 to 22.07.2010 at 23:18:01 and from 05.09.2010 at 01:20:00 to 10.08.2011 at 04:58:00 (with a measurement every 120 seconds). This ASPEX dataset can be downloaded from here: a zip file containing one .txt file with indications of recording time, location and water depth of the two moorings and four data files (one .txt file per mooring and per recorded period) with for each measurement the year (YYYY), month (MM), day (DD), hour (hh), minute (mm) second (ss) and pressure (P), temperature (T), conductivity (C) and salinity (S) values. As part of the PAMELA project, 18 XBT (eXpendable BathyThermograph) probes (Sippican) were launched in 2013 (July to September) offshore Aquitaine Basin. Seawater temperature profiles were thus acquired through the water column from different locations at the shelf area (at 140 m water depth), the continental slope and the basin (at 1213 m water depth) (Fig. A). Some of these XBT profiles are accessible via the Coriolis platform (http://www.coriolis.eu.org/). The complete GAZCOGNE1-2 dataset can be downloaded from here: a zip file containing one .txt file with indications of time, location and water depth for the XBTs and 18 data files (one .txt file per XBT profile). All times are in UTC.
-

This raster dataset represents physical disturbance to the seabed in the European seas. Several human activities disturb the seabed either directly or indirectly. Alteration of benthic living conditions as a result of increased sedimentation or attenuation of light penetration, abrasion of the seabed and exploitation of benthic biota, temporarily disturb the benthic habitat quality. The dataset is an aggregation of several different human activities that cause physical disturbance to the seabed: aquaculture, demersal fishing, dredging and dumping of dredged material, oil and gas rigs, offshore installations, ports, sand and gravel extraction, shellfish mariculture, shipping in shallow waters and windfarms. The resulting dataset is a raster (10km grid cell) derived from EMODnet, MED-IAMER, JRC-STECF, OSPAR, HELCOM and 4C Offshore datasets, and with reference temporal coverage from 2012 to 2017. This dataset has been prepared for the calculation of the combined effect index, produced for the ETC/ICM Report 4/2019 "Multiple pressures and their combined effects in Europe's seas" available on: https://www.eionet.europa.eu/etcs/etc-icm/etc-icm-report-4-2019-multiple-pressures-and-their-combined-effects-in-europes-seas-1.
 Metadata catalogue
Metadata catalogue