Tool
Type of resources
Topics
INSPIRE themes
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Representation types
-

The indiSeaS project is co-funded by the Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission (IOC), the European Network of Excellence Euroceans, “'Institut de recherche pour le développement (IRD)” and the European project on Marine Ecosystem Evolution in a Changing Environment (MEECE). It is a multi-institutes collaborative effort. Scientific experts on ecosystems all over world calculate indicators and provide background information. The IndiSeas project aims at "Evaluating the status of marine ecosystems in a changing world”, using a set of different types of indicators to reflect the effects of multiple drivers on the states and trends of marine exploited ecosystems. It focuses on the effects of fishing, use of ecology, biodiversity, as well as climate and socio-economic indicators on world's marine ecosystems health. The objectives are to review IndiSeas datasets, present preliminary results to regional experts, discuss methods to be developed in each of the six task groups, establish work and publication plans for the future. Expertise from over 70 scientists, 49 research institutes and 36 countries.
-
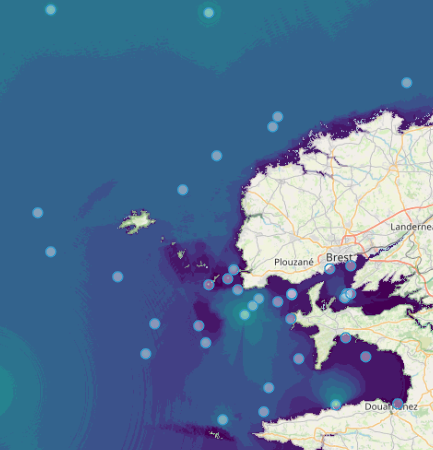
Quonops Online Services provide noise monitoring and prediction tools. In a similar manner to weather forecasting systems, Quonops© produces an estimate of the spatio-temporal distribution of noise levels generated by human activities at sea, aggregating multiple sources, and assessing short-, mid- and long-term source contributions to the global noise field. The outputs from Quonops© are tailored to the requirements of existing and emerging national and international regulations regarding: - Underwater noise. - The conservation of habitats and marine ecosystems. - The protection of marine species. Such tools aim to support management decisions by assessing, quantifying and prioritizing direct and indirect anthropogenic pressures on marine life, according to regulations on underwater noise, especially the descriptor 11 of the European Marine Strategy Framework Directive.
-
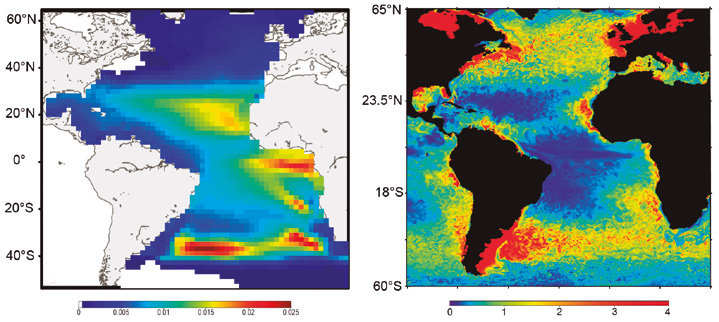
SEAPODYM has been initiated in the mid-1990s by the Oceanic Fisheries Programme of the Secretariat of the Pacific Community (SPC) and developed under several European development projects. The objective was to propose new management tools taking into account both the fishing impact and environmental variability. Since 2006, in partnership with SPC, its development has continued with the Marine Ecosystem Modeling team of CLS (Collecte Localisation Satellite). CLS aims to combine this modeling approach with satellite observation and real-time data collection to develop operational real-time applications and advise government administrations on the sustainable management and monitoring of marine resources. The main features of SEAPODYM framework are: - Prediction of the temporal and spatial distributions of functional lower and mid-trophic level groups (Lehodey et al. 2010; 2015) - Prediction of the temporal and spatial distributions of age-structured predator (fish) populations (Lehodey et al. 2008); - Prediction of the total catch and the size-frequency of catch by fishing fleet; - Parameter optimization based on data assimilation techniques (Senina et al., 2008); The lower and mid-trophic level (LMTL) sub-model describes the dynamics of a functional group of zooplankton and several vertically migrant and non-migrant micronekton (prey of larger fish) groups. The dynamics are linked to temperature and currents. Assimilation of acoustic or biomass data is used to estimate the model parameters. The dynamics of fish populations are estimated using habitat indices, movements, growth and mortality. The feeding habitat is based on the accessibility of fish to the groups of prey. The spawning habitat combines temperature preference and coincidence of spawning with presence or absence of predators and food for larvae. Successful larval recruitment is linked to spawning stock biomass and mortality during the drift with currents. Older fish can swim along the gradient of habitat index in addition to being advected by ocean currents.
-

The Department of Environment, Forestry and Fisheries (DEFF) and the Department of Science and Innovation (DSI) have initiated the development of the National Oceans and Coastal Information Management System (OCIMS) for South Africa – referred to as the OCIMS project. The OCIMS project forms part of the Operation Phakisa Marine Protection Services and Oceans Governance workstream Initiative 6: “National Ocean and Coastal Information System and Extending Earth Observation Capability” action plan that is endorsed by Cabinet. Operation Phakisa focuses on unlocking the economic potential of South Africa’s oceans. OCIMS will support a variety of oceans and coastal initiatives by providing information and decision support to key stakeholders for the day-to-day management of South Africa’s oceans and coasts. The project outcomes will be achieved through the development of an Information Management System (IMS) that will integrate current and future oceans and coastal systems, information and expertise into a user-friendly and cost-effective IMS for the benefit of relevant stakeholders. In June 2015, the Council for Science and Industrial Research (CSIR) was nominated by DEFF as a service provider to facilitate the implementation of the project and to co-develop OCIMS. OCIMS project vision: Develop a locally relevant and globally cognisant technological solution that supports the ecological conservation and economic potential of South Africa’s oceans and coasts through information and decision-support for effective governance.
-

The Sea Around Us is a research initiative at The University of British Columbia (located at the Institute for the Oceans and Fisheries, formerly Fisheries Centre) that assesses the impact of fisheries on the marine ecosystems of the world, and offers mitigating solutions to a range of stakeholders. The Sea Around Us was initiated in collaboration with The Pew Charitable Trusts in 1999, and in 2014, the Sea Around Us also began a collaboration with The Paul G. Allen Family Foundation to provide African and Asian countries with more accurate and comprehensive fisheries data. It provides data and analyses through View Data, articles in peer-reviewed journals, and other media (News). We regularly update our products at the scale of countries’ Exclusive Economic Zones, Large Marine Ecosystems, the High Seas and other spatial scales, and as global maps and summaries. It emphasises catch time series starting in 1950, and related series (e.g., landed value and catch by flag state, fishing sector and catch type), and fisheries-related information on every maritime country (e.g., government subsidies, marine biodiversity). Information is also offered on sub-projects, e.g., the historic expansion of fisheries, the performance of Regional Fisheries Management Organizations, or the likely impact of climate change on fisheries. The information and data presented on this website is freely available to any user, granted that its source is acknowledged. We are aware that this information may be incomplete. Please let us know about this via the feedback options available on this website.
-

The EuroMapApp task of the AtlantOS project aims to integrate Europe’s existing and future bathymetric data sets from the Atlantic Ocean into a seamless whole and put these results into a widely accessible format allowing immediate visualization of the seafloor for the specialist and non-specialist user alike. The partner institutions are GEOMAR, Ifremer, NIOZ, and NERC-BODC.
-
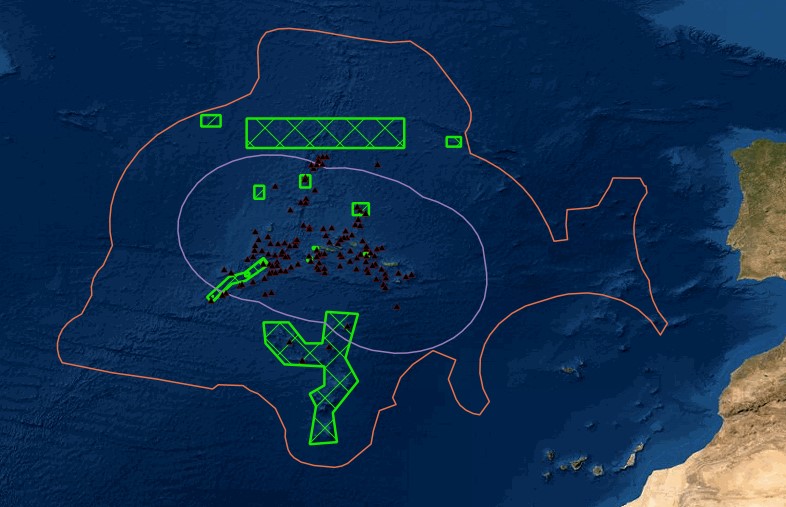
Portal of Maritime Spatial Planning of the Azores which hosts several GIS layers, such as: - Fishing areas and aquaculture production areas - Bathymetry - Mineral resources: Deep seabed polymetallic nodules - Hydrothermal vents - Distribution of seamount extracted, 2008 - Seafloor geomorphologic classification - Ocean environmental variables mean between the years 2002 and 2013: Sea Surface Temperature, Chlorophyll-a Concentration, Particulate Organic Carbon and Particulate Inorganic Carbon, Photosynthetically, Available Radiation, Ocean Productivity - Maerl habitats - Predictive distribution modelling for 26 cold-water coral species - Coldwater corals - Legal issues - Infrastructure and equipment - Underwater cultural heritage - Aggregate extraction - Tourist maritime activities
 Metadata catalogue
Metadata catalogue