Biological data
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
INSPIRE themes
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
status
Resolution
-
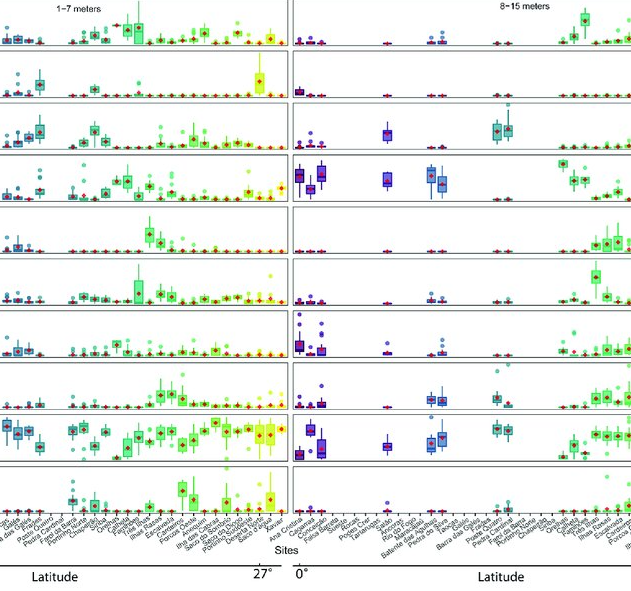
As marine ecosystems are influenced by global and regional processes, standardized information on community structure has become crucial for assessing broad-scale responses to natural and anthropogenic disturbances. Extensive biogeographic provinces, such as the Brazilian Province in the southwest Atlantic, present numerous theoretical and methodological challenges for understanding community patterns on a macroecological scale. In particular, the Brazilian Province is composed of a complex system of heterogeneous reefs and a few offshore islands, with contrasting histories and geophysical-chemical environments. Despite the large extent of the Brazilian Province (almost 8,000 kilometers), most studies of shallow benthic communities are qualitative surveys and/or have been geographically restricted. We quantified community structure of shallow reef habitats from 0° to 27°S latitude using a standard photographic quadrat technique. Percent cover data indicated that benthic communities of Brazilian reefs were dominated by algal turfs and frondose macroalgae, with low percent cover of reef-building corals. Community composition differed significantly among localities, mostly because of their macroalgal abundance, despite reef type or geographic region, with no evident latitudinal pattern. Benthic diversity was lower in the tropics, contrary to the general latitudinal diversity gradient pattern. Richness peaked at mid-latitudes, between 20°S to 23°S, where it was ~3.5-fold higher than localities with the lowest richness. This study provides the first large-scale description of benthic communities along the southwestern Atlantic, providing a baseline for macroecological comparisons and evaluation of future impacts. Moreover, the new understanding of richness distribution along Brazilian reefs will contribute to conservation planning efforts, such as management strategies and the spatial prioritization for the creation of new marine protected areas.
-
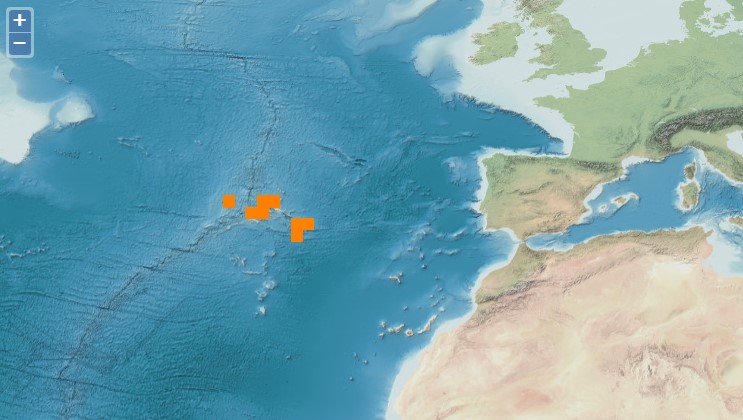
Fish assemblages surveyed by using underwater visual censuses (UVC) down to 40 m. Transects were performed between 1997 and 2015 in the Azores, Portugal. All mobile fish were identified to the lowest possible taxon. Dates, geographic coordinates and species recorded are provided. Fish assemblages were surveyed using underwater visual censuses (UVC) down to 40 m. Following standard belt transect surveys (Brock 1954), SCUBA divers sampled transects with 50 m length and 5 m width. All mobile fish were identified to the lowest possible taxon and counted. Sampling sites were chosen based on the general representativeness of the habitat. Transects within sites were selected by stratified random sampling: different transects were done in each dive without replicating the depth strata (every 10 m) or overall bottom type or crossing transects during a single dive or day. UVCs were conducted in the scope of projects CLIPE (FCT—Praxis XXI/3/3.2/EMG/1957/95), MARÉ (LIFE B4-3200/98-509), MAREFISH (FCT-POCTI/ BSE/41207/2001), OGAMP (INTERREG IIIb/MAC/4.2/A2 2001), MARMAC (INTERREGIIIb-03/MAC/4.2/A1 2004), EmpaFish (EC-FP6, SSP8-006539), MareFish (FCT, POCTI/BSE/41207/2001), MoniZEC (FRC - M2.1.2/I/018/2011)
-

Reef fish represent one of the most diverse vertebrate groups on Earth, with over 7,000 species distributed around the globe. This richness is not evenly distributed geographically. The Atlantic (AT) and the Eastern Pacific (EP) encompass 30% of the global fish fauna. These areas have been considered the most isolated from the marine biodiversity hotspot in the Indo-Pacific due to distinct physical barriers, such as the Tethyan closure and the distance between the EP and the western Pacific. Despite their comparatively lower species richness, these realms host unique fish assemblages characterized by a remarkable proportion of regional endemics and species with large body size. Here, we present the largest database of life-history traits and biogeographical and conservation aspects presently available for the reef fish fauna of the AT and the EP realms. The database includes 21 traits distributed into behavioral (home range, diel activity, group size, level in the water column, three measures of preferred temperature), morphological (maximum body size, size class, body shape, aspect ratio, caudal fin, mouth position), and ecological (trophic level, diet, spawning strategy, depth of occurrence, two allometric constants, pelagic larval duration, and life span), as well as biogeographical (geographic range index, range extension, species distribution in 20 marine provinces, latitude north and south of occurrence, total number of provinces where species occur, occurrence in the AT and EP), and conservation aspects (IUCN status, vulnerability and global market price). We compiled these data through a careful review of 104 local checklists published between 1982 and 2020, online repositories, local reports, books, and monographs on specific families or genera. We limited our database to localities situated between latitudes 51°N and 45°S that including shallow and upper mesophotic biogenic and/or rocky reefs habitats. Our database covers 2,198 species belonging to 146 families and 655 reef fish genera distributed in two marine realms (1,458 in the AT, 829 in the EP, and 89 in both realms) and 20 marine provinces. This database of reef fish offers the opportunity to explore novel ecological and evolutionary questions at different scales and provides tools for species conservation based on these traits. There are no copyright or proprietary restrictions for research or teaching purposes.
-
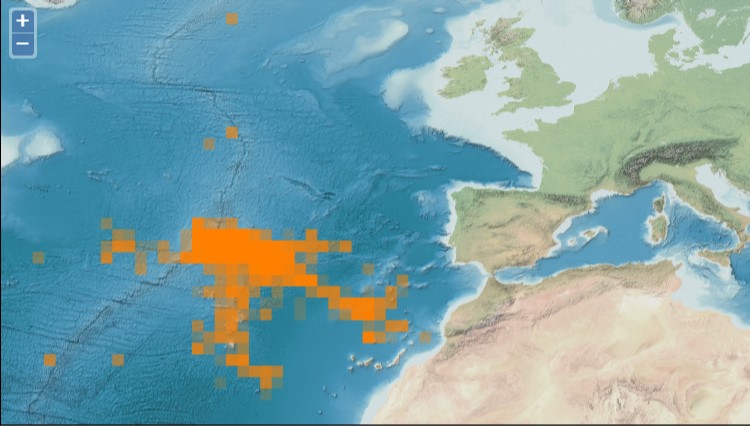
Sightings of birds were recorded daily, at 6 different fixed periods (snap shots), when the boat was in navigation or search mode. POPA was launched in 1998 with the main goal of certifying the tuna caught around the Azores as a "dolphin safe product". This label is attributed by the non-governmental organization Earth Island Institute to catches made without mortality of cetaceans. POPA has built an extensive database with information collected by the observers on board the tuna fishing vessels. This database includes information on tuna fisheries (e.g., location of fishing events, catches, and fishing effort), weather conditions (e.g., sea surface temperature, wind and visibility), live bait fisheries (e.g., location of fishing events, catches, gears used), cetaceans (e.g., occurrences, interaction with fishing events and association with other species), birds and sea turtles (e.g., occurrences). POPA is also responsible for "Friend of the Sea" tuna fishery certification. In the late 1990’s, it became clear that the tuna industry would be seriously penalized with the absence of a "dolphin safe" certification which instigated new measures from the government and the fisheries sector. In order to achieve this certification, the Azores Fisheries Observer Programme (POPA) was funded in 1998, ensuring the absence of dolphin mortality or injury in tuna fishery. Since then, fishery and fishing products are certified by the Earth Island Institute, through the results presented by POPA. Besides that, the tuna fishery is also certified as "Friend of the Sea" which means that it is extremely selective, doesn’t harm the surrounding environment and is quite sustainable. It became the first tuna fishery in the world achieving that certification. The Programme results from an agreement among Regional Administration, Earth Island Institute, the Tuna Canning Industry Association (Pão do Mar), the Fishing Boat Owners Association (APASA) and IMAR - Instituto do Mar - through the University of The Azores Center (IMAR-DOP/Uaç), which carries out the programme. Until 2003, the Programme was supported by regional funds. Between 2003 and 2005 it became co-financed by the European Commission through the INTERREG IIIb Programme/ ORPAM project. Since then it has been exclusively supported by the regional government through the Regional Secretary of Fisheries.
-
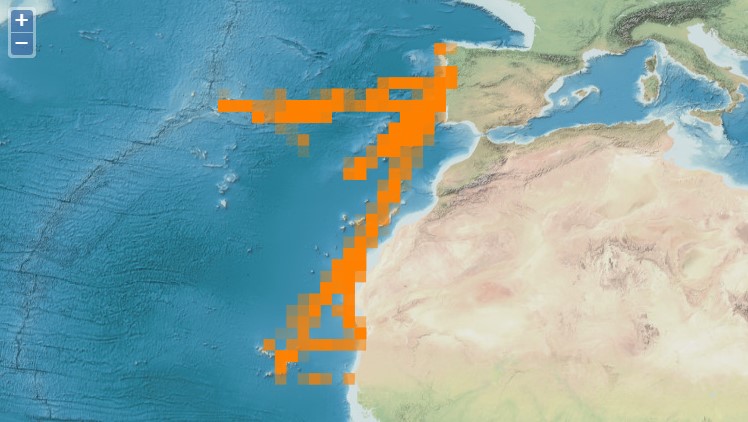
The CETUS dataset contains effort-based occurrence records collected during a cetacean monitoring programme in the Eastern North Atlantic, since 2012. The CETUS dataset contains data collected within the CETUS Project (www.cetusproject.com), a cetacean monitoring programme in the Eastern North Atlantic, running since 2012. The project is led by the Interdisciplinary Centre of Marine and Environmental Research (CIIMAR - University of Porto, Portugal), in partnership with TRANSINSULAR - Grupo ETE, a Portuguese company for maritime transport, that offers its cargo ships to be used as a platforms of opportunity to monitor cetaceans along routes between Continental Portugal and Madeira, Azores, Canary and Cape Verde islands. On-board trained marine mammal observers collect data on: survey effort, cetacean and other megafauna occurrences, as well as marine traffic and meteorological conditions. Data is provided in the recent OBIS-ENV-DATA format, and comprises 8913 georeferenced positions associated with 3195 occurrences of 44 marine taxa.
-
Sightings (snap shots) of marine mammals collected by Biosphere Expeditions collaborators specifically for POPA. Since 2004 Biosphere Expeditions (www.biosphere-expeditions.org) collects data for POPA in the Azores central group in April and May. POPA was launched in 1998 with the main goal of certifying the tuna caught around the Azores as a "dolphin safe product". This label is attributed by the non-governmental organization Earth Island Institute to catches made without mortality of cetaceans. POPA has built an extensive database with information collected by the observers on board the tuna fishing vessels. This database includes information on tuna fisheries (e.g., location of fishing events, catches, and fishing effort), weather conditions (e.g., sea surface temperature, wind and visibility), live bait fisheries (e.g., location of fishing events, catches, gears used), cetaceans (e.g., occurrences, interaction with fishing events and association with other species), birds and sea turtles (e.g., occurrences). POPA is also responsible for "Friend of the Sea" tuna fishery certification. In the late 1990’s, it became clear that the tuna industry would be seriously penalized with the absence of a "dolphin safe" certification which instigated new measures from the government and the fisheries sector. In order to achieve this certification, the Azores Fisheries Observer Programme (POPA) was funded in 1998, ensuring the absence of dolphin mortality or injury in tuna fishery. Since then, fishery and fishing products are certified by the Earth Island Institute, through the results presented by POPA. Besides that, the tuna fishery is also certified as "Friend of the Sea" which means that it is extremely selective, doesn’t harm the surrounding environment and is quite sustainable. It became the first tuna fishery in the world achieving that certification. The Programme results from an agreement among Regional Administration, Earth Island Institute, the Tuna Canning Industry Association (Pão do Mar), the Fishing Boat Owners Association (APASA) and IMAR - Instituto do Mar - through the University of The Azores Center (IMAR-DOP/Uaç), which carries out the programme. Until 2003, the Programme was supported by regional funds. Between 2003 and 2005 it became co-financed by the European Commission through the INTERREG IIIb Programme/ ORPAM project. Since then it has been exclusively supported by the regional government through the Regional Secretary of Fisheries.
-

To assess the status of the South and Tropical Atlantic marine ecosystem and develop a framework for predicting its future changes, from months to decades, by combining ecosystem observations, climate-based ecosystem prediction and information on future socio-economic and ecosystem service changes, and thus to contribute to the sustainable management of human activities in the Atlantic Ocean as a whole. TRIATLAS contributes to this by delivering knowledge of the current state and future changes of the Atlantic marine ecosystems. We achieve this goal through a basin-wide approach that integrates research from the North and South, and that closes critical knowledge gaps in the Tropical and South Atlantic that impede an understanding of the entire basin. 33 partners from 13 countries Project duration: June 2019 – May 2023 Monthly model biomass values for the best fitted Ecosim model of the Southern Benguela ecosystem for the period 1978-2015. The model was driven by fishing effort/mortality and a forcing function applied to phytoplankton, based on a cumulative upwelling index, and was fitted to available catch and abundance time-series data.
-

Information collected by the observers on board the tuna fishing vessels on tuna fisheries, weather conditions, live bait fisheries, cetaceans, birds and sea turtles. POPA was launched in 1998 with the main goal of certifying the tuna caught around the Azores as a "dolphin safe product". This label is attributed by the non-governmental organization Earth Island Institute to catches made without mortality of cetaceans. POPA has built an extensive database with information collected by the observers on board the tuna fishing vessels. This database includes information on tuna fisheries (e.g., location of fishing events, catches, and fishing effort), weather conditions (e.g., sea surface temperature, wind and visibility), live bait fisheries (e.g., location of fishing events, catches, gears used), cetaceans (e.g., occurrences, interaction with fishing events and association with other species), birds and sea turtles (e.g., occurrences). POPA is also responsible for "Friend of the Sea" tuna fishery certification. In the late 1990’s, it became clear that the tuna industry would be seriously penalized with the absence of a "dolphin safe" certification which instigated new measures from the government and the fisheries sector. In order to achieve this certification, the Azores Fisheries Observer Programme (POPA) was funded in 1998, ensuring the absence of dolphin mortality or injury in tuna fishery. Since then, fishery and fishing products are certified by the Earth Island Institute, through the results presented by POPA. Besides that, the tuna fishery is also certified as "Friend of the Sea" which means that it is extremely selective, doesn’t harm the surrounding environment and is quite sustainable. It became the first tuna fishery in the world achieving that certification. The Programme results from an agreement among Regional Administration, Earth Island Institute, the Tuna Canning Industry Association (Pão do Mar), the Fishing Boat Owners Association (APASA) and IMAR - Instituto do Mar - through the University of The Azores Center (IMAR-DOP/Uaç), which carries out the programme. Until 2003, the Programme was supported by regional funds. Between 2003 and 2005 it became co-financed by the European Commission through the INTERREG IIIb Programme/ ORPAM project. Since then it has been exclusively supported by the regional government through the Regional Secretary of Fisheries.
-
The Continuous Plankton Recorder (CPR) Survey is the most geographically extensive marine monitoring programme in the world. Today the Survey is operated by the Marine Biological Association, based in Plymouth, UK. Operating since 1931, the Continuous Plankton Recorder (CPR) survey is recognised as the longest sustained and geographically most extensive marine biological survey in the world. The dataset comprises a uniquely large record of marine biodiversity covering ~800 taxa over multi-decadal periods. In terms of our scientific understanding of natural variability and human-induced change on our oceans, the CPR survey is of global importance and it is used by scientists, policy makers and environmental managers across the world. The data is used to examine strategically important science pillars such as climate change, human health, fisheries, biodiversity, pathogens, invasive species, ocean acidification and natural capital. The results have included the globally first documented studies of large-scale ecological regime shifts, and of biogeographic, phenological and trans-arctic migrations in the marine environment in response to climate change. The data in this sampling event resource has been published as a Darwin Core Archive (DwC-A), which is a standardized format for sharing biodiversity data as a set of one or more data tables. The core data table contains 252,385 records. 2 extension data tables also exist. An extension record supplies extra information about a core record. The number of records in each extension data table is illustrated below.
-

We developed predictive distribution models of deep-sea elasmobranchs for up to 2000 m depth in the Azores EEZ and neighboring seamounts, from approximately 33°N to 43°N and 20°W to 36°W. Georeferenced presence, absence, and abundance data were obtained from scientific surveys and commercial operations reporting at least one deep-sea elasmobranch capture. A 20-year 'survey dataset' (1996-2017) was compiled from annual scientific demersal surveys using two types of bottom longlines (types LLA and LLB), and an 'observer dataset' (2004-2018) from observer programs covering commercial fisheries operations using bottom longline (similar to type LLA) and vertical handline ('gorazeira').
 Metadata catalogue
Metadata catalogue