Article
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
INSPIRE themes
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
status
Scale
-

We assembled a dataset of 14C-based productivity measurements to understand the critical variables required for accurate assessment of daily depth-integrated phytoplankton carbon fixation (PP(PPeu)u) from measurements of sea surface pigment concentrations (Csat)(Csat). From this dataset, we developed a light-dependent, depth-resolved model for carbon fixation (VGPM) that partitions environmental factors affecting primary production into those that influence the relative vertical distribution of primary production (Pz)z) and those that control the optimal assimilation efficiency of the productivity profile (P(PBopt). The VGPM accounted for 79% of the observed variability in Pz and 86% of the variability in PPeu by using measured values of PBopt. Our results indicate that the accuracy of productivity algorithms in estimating PPeu is dependent primarily upon the ability to accurately represent variability in Pbopt. We developed a temperature-dependent Pbopt model that was used in conjunction with monthly climatological images of Csat sea surface temperature, and cloud-corrected estimates of surface irradiance to calculate a global annual phytoplankton carbon fixation (PPannu) rate of 43.5 Pg C yr‒1. The geographical distribution of PPannu was distinctly different than results from previous models. Our results illustrate the importance of focusing Pbopt model development on temporal and spatial, rather than the vertical, variability.
-

The largest landings in this ecoregion are by Norway, the Russian Federation (Russia henceforth), Faroe Islands, and Iceland, mainly by pelagic fisheries. Other nations also have fisheries in the area. The number of fishing vessels is declining while the size of the remaining vessels is increasing. The annual catch in the ecoregion has varied between 700 000 tonnes to over 2 million tonnes. The pelagic fisheries, using purse seine and pelagic trawls, account for the largest catches by weight and target herring (her.27.1-24a514a), blue whiting (whb.27.1-91214), mackerel (mac.27.nea), and other pelagic species. The largest demersal fishery targets cod (cod.27.1-2), haddock (had.27.1-2), and saithe (pok.27.1-2) using bottom trawls, purse seine, Danish seine and gillnets, and to a lesser extent hook and line gear. Smaller fisheries target other gadoid species, Greenland halibut (ghl.27.1-2), and redfish. Landings of pelagic species within the ecoregion in the last decades have been variable. The demersal fisheries, dominated by cod, display less pronounced fluctuations than the pelagic fisheries. Information about discards is sparse, but the total weight of discards is considered low in both the pelagic and the demersal fisheries. Harp seals and minke whales are hunted in the region. Status summary of Norwegian Sea stocks relative to the ICES maximum sustainable yield (MSY) approach and precautionary approach (PA) is known for 50% of the 23 stocks assessed by ICES in this ecoregion. Only 22% of the stocks are fished below FMSY, accounting for nearly 13% of the total catch. 30% of the stocks have a biomass above MSY Btrigger, accounting for 86% of the total catch. Demersal stocks have shown a trend of declining fishing mortality since the mid-1990s, and the average F/FMSY ratio is now close to 1. The mean SSB/MSY Btrigger ratio of demersal stocks has been decreasing over the last decade, but mean SSB remains above MSY Btrigger. The average F/FMSY ratio for pelagic stocks has been decreasing since 2000 and is now close to 1. The mean SSB/MSY Btrigger ratio for pelagic species has shown a slight increase over the last two decades and is above 1. In addition to biomass removal, ecosystem effects of fisheries include abrasion, ghost fishing, and bycatch of protected, endangered, and threatened species.
-
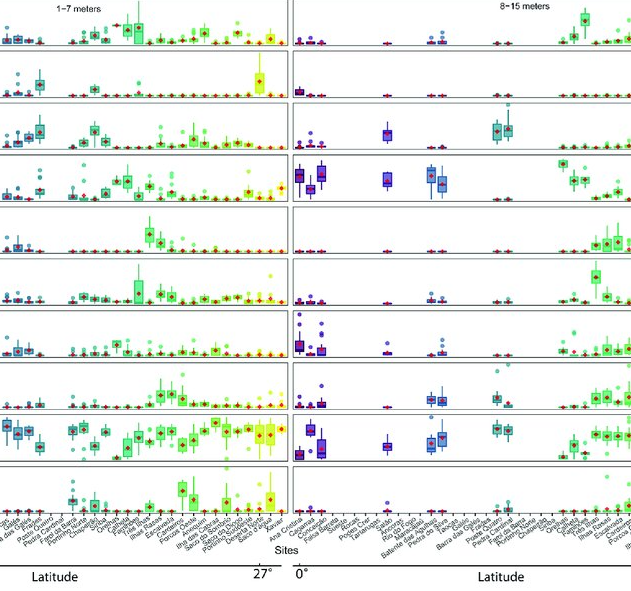
As marine ecosystems are influenced by global and regional processes, standardized information on community structure has become crucial for assessing broad-scale responses to natural and anthropogenic disturbances. Extensive biogeographic provinces, such as the Brazilian Province in the southwest Atlantic, present numerous theoretical and methodological challenges for understanding community patterns on a macroecological scale. In particular, the Brazilian Province is composed of a complex system of heterogeneous reefs and a few offshore islands, with contrasting histories and geophysical-chemical environments. Despite the large extent of the Brazilian Province (almost 8,000 kilometers), most studies of shallow benthic communities are qualitative surveys and/or have been geographically restricted. We quantified community structure of shallow reef habitats from 0° to 27°S latitude using a standard photographic quadrat technique. Percent cover data indicated that benthic communities of Brazilian reefs were dominated by algal turfs and frondose macroalgae, with low percent cover of reef-building corals. Community composition differed significantly among localities, mostly because of their macroalgal abundance, despite reef type or geographic region, with no evident latitudinal pattern. Benthic diversity was lower in the tropics, contrary to the general latitudinal diversity gradient pattern. Richness peaked at mid-latitudes, between 20°S to 23°S, where it was ~3.5-fold higher than localities with the lowest richness. This study provides the first large-scale description of benthic communities along the southwestern Atlantic, providing a baseline for macroecological comparisons and evaluation of future impacts. Moreover, the new understanding of richness distribution along Brazilian reefs will contribute to conservation planning efforts, such as management strategies and the spatial prioritization for the creation of new marine protected areas.
-

Assessments run at AFWG provide the scientific basis for the management of cod, haddock, saithe, redfish, Greenland halibut and capelin in subareas 1 and 2. Taking the catch values provided by the Norwegian fisheries ministry for Norwegian catches1 and raising the total landed value to the total catches gives an approximate nominal first-hand landed value for the combined AFWG stocks of ca. 20 billion NOK or ca. 2 billion EUR (2018 estimates).
-
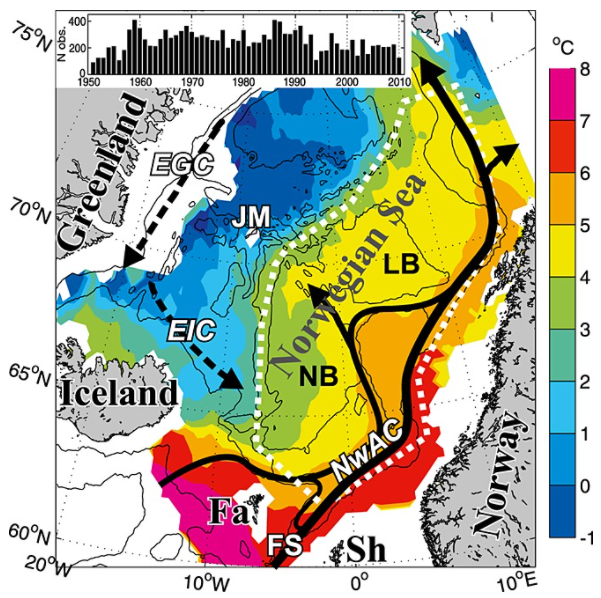
Climate variability in the Norwegian Sea was investigated in terms of ocean heat and freshwater contents of Atlantic water above a reference surface, using hydrographic data during spring 1951–2010. The main processes acting on this variability were examined and then quantified. The area-averaged water mass cooled and freshened, but a deepening of the reference surface resulted in a positive trend in the heat content of 0.3 W m−2. Air-sea heat fluxes explained about half of the interannual variability in heat content. The effect of the advection of Atlantic and Arctic waters on the variability varied with time, apparently due to large-scale changes in the ocean circulation. The data are consistent with the explanation that changing wind patterns caused buffering and then release of Arctic water in the Iceland Sea during the late 1960s to early 1970s, and this caused large hydrographic changes in the Norwegian Sea.
-

-

As a consequence of the impact of the COVID pandemic on international travel which prevented the traditional meeting from taking place, the Working Group on Widely Distributed Stocks (WGWIDE) met online via WebEx hosted by ICES. Prior to the 2020 meeting, the generic ToRs for species and regional working groups were re-prioritised by ACOM to allow the WG to focus primarily on those ToRs most applicable to the provision of advice. WGWIDE reports on the status and considerations for management of Northeast Atlantic mackerel, blue whiting, Western and North Sea horse mackerel, Northeast Atlantic boarfish, Norwegian springspawning herring, striped red mullet (Subareas 6, 8 and Divisions 7.a-c, e-k and 9.a), and red gurnard (Subareas 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, and 8) stocks. Northeast Atlantic (NEA) Mackerel. This stock is highly migratory and widely distributed throughout the Northeast Atlantic with significant fisheries is most ICES subareas. A diverse range of fleets from smaller artisanal, handline vessels to large (100m+) factory freezer vessels and modern RSW trawlers and purse seiners take part in what is one of the most valuable European fisheries. The assessment conducted in 2020 is an update assessment, based on the configuration agreed during the most recent inter-benchmark exercise in 2019 and incorporates the most recent data available from sampling of the commercial catch in 2019, the final 2019 egg survey SSB estimate, an updated recruitment index and tagging time series along with 2020 survey data from the IESSNS swept area survey. Advice is given based on stock reference points which were updated during a management strategy evaluation carried out in 2020. Following a strong increase from 2007 to 2014, SSB has been declining although it remains well above MSY Btrigger. Fishing mortality has been below FMSY since 2016. There have been a number of large year classes since 2001 with above average recruitment over much of the most recent decade. Blue Whiting. This pelagic gadoid is widely distributed in the eastern part of the North Atlantic. The 2020 update assessment followed the protocol from the most recent inter-benchmark in 2016 and used preliminary catch data from 2020. Due to the cancellation of the 2020 acoustic survey, this data was not available. The effect on the assessment was minimal and limited to increases in uncertainty of the terminal year estimates. The SSB continues to decrease from the most recent maximum in 2017 mainly due to below average recruitment since 2017, although it remains above MSY Btrigger. Fishing mortality has been above FMSY since 2014. Norwegian Spring Spawning Herring. This is one of the largest herring stocks in the world. It is highly migratory, spawning along the Norwegian coast and feeding throughout much of the Norwegian Sea. The 2020 assessment is based on an implementation of the XSAM assessment model introduced at the benchmark in 2016. This years’ assessment indicates that the stock is continuing to decline from the peak in 2008 of 7Mt to just above MSY Btrigger due to successive years of average or below average recruitment. Catch advice for 2021 is given on the basis of the agreed management plan and represents a substantial increase over the 2020 advice due to an upward revision in the estimate of the 2016 year-class which is considered to be the most significant year-class since 2004.
-

Reef fish represent one of the most diverse vertebrate groups on Earth, with over 7,000 species distributed around the globe. This richness is not evenly distributed geographically. The Atlantic (AT) and the Eastern Pacific (EP) encompass 30% of the global fish fauna. These areas have been considered the most isolated from the marine biodiversity hotspot in the Indo-Pacific due to distinct physical barriers, such as the Tethyan closure and the distance between the EP and the western Pacific. Despite their comparatively lower species richness, these realms host unique fish assemblages characterized by a remarkable proportion of regional endemics and species with large body size. Here, we present the largest database of life-history traits and biogeographical and conservation aspects presently available for the reef fish fauna of the AT and the EP realms. The database includes 21 traits distributed into behavioral (home range, diel activity, group size, level in the water column, three measures of preferred temperature), morphological (maximum body size, size class, body shape, aspect ratio, caudal fin, mouth position), and ecological (trophic level, diet, spawning strategy, depth of occurrence, two allometric constants, pelagic larval duration, and life span), as well as biogeographical (geographic range index, range extension, species distribution in 20 marine provinces, latitude north and south of occurrence, total number of provinces where species occur, occurrence in the AT and EP), and conservation aspects (IUCN status, vulnerability and global market price). We compiled these data through a careful review of 104 local checklists published between 1982 and 2020, online repositories, local reports, books, and monographs on specific families or genera. We limited our database to localities situated between latitudes 51°N and 45°S that including shallow and upper mesophotic biogenic and/or rocky reefs habitats. Our database covers 2,198 species belonging to 146 families and 655 reef fish genera distributed in two marine realms (1,458 in the AT, 829 in the EP, and 89 in both realms) and 20 marine provinces. This database of reef fish offers the opportunity to explore novel ecological and evolutionary questions at different scales and provides tools for species conservation based on these traits. There are no copyright or proprietary restrictions for research or teaching purposes.
-

Morphological map (10 classes) of the Irish shelf resulting from the modal aggregation (Cell statistics “MAJORITY” in ArcGIS Pro 3.1) of the qualitatively and quantitatively best Fully Convolutional Neural Networks models obtained in the study: Arosio, R., Hobley, B., Wheeler, A. J., Sacchetti, F., Conti, L. A., Furey, T. and A. Lim, 2023. Fully convolutional neural networks applied to large-scale marine morphology mapping. Frontiers in Marine Science, Sec. Ocean Observation, 10, https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2023.1228867.
 Metadata catalogue
Metadata catalogue