Aggregate data
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
-
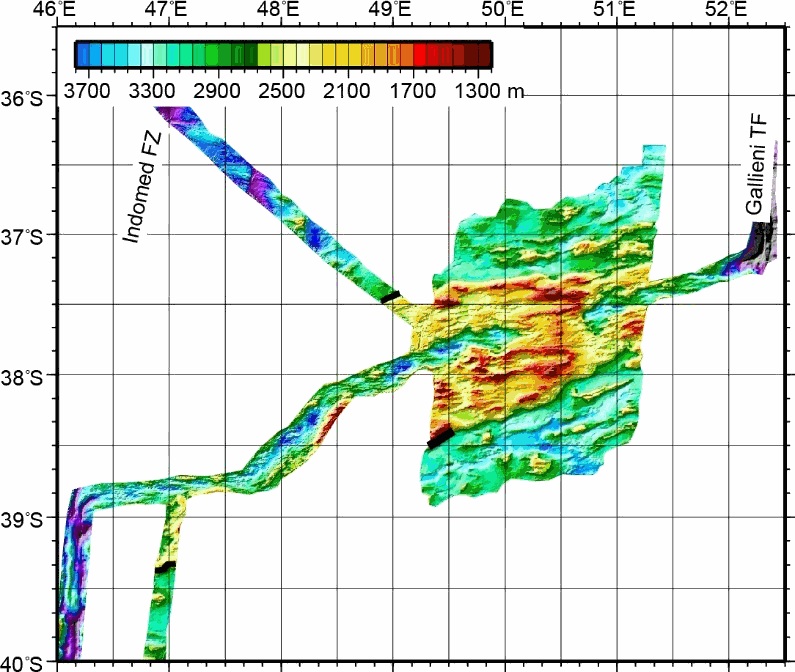
This grid was obtained by merging multibeam bathymetric data from several french cruises along the Southwest Indian Ridge from the Indomed to the Gallieni Transform Faults. The spatial resolution is about 150 m. This dataset was used in several scientific papers.
-
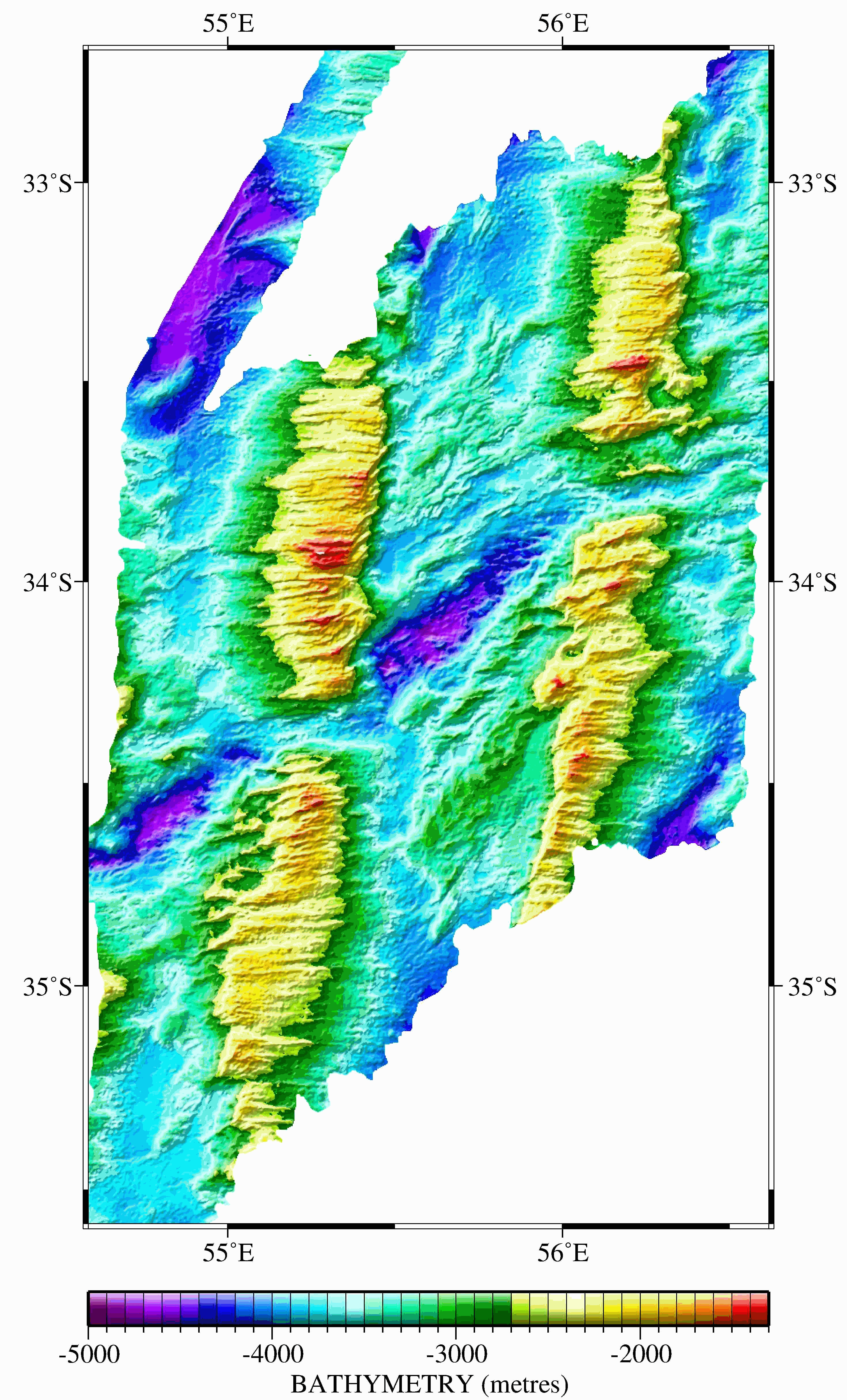
Six large grids were obtained by merging multibeam bathymetric data from several international cruises along the Southwest Indian Ridge from the Gallieni Transform Fault (54°E) to the Rodrigues Triple Junction (70°E). The spatial resolution is about 150 m. This dataset was used in several scientific papers.
-
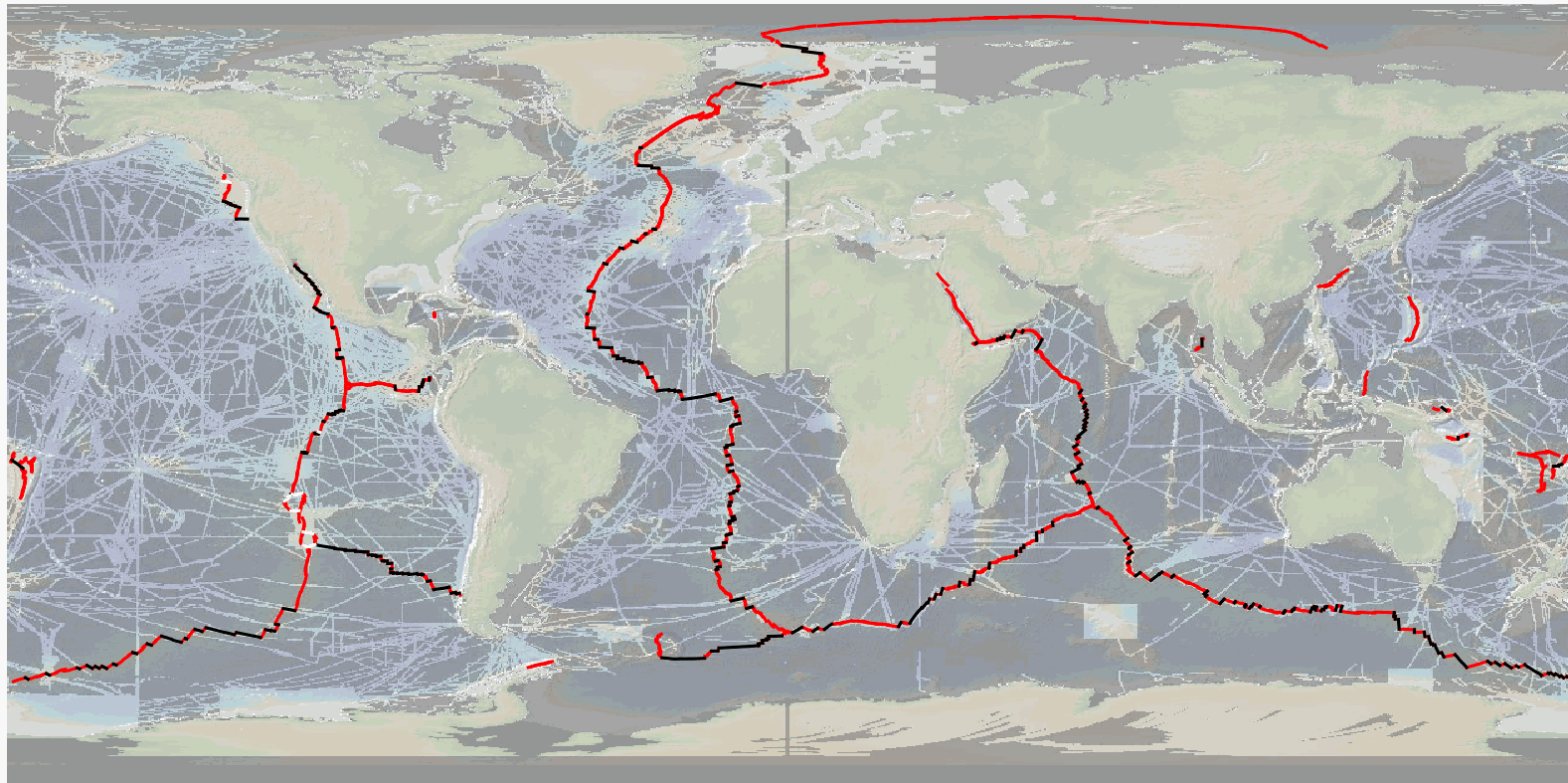
The precise location and geometry of oceanic spreading centers and associated transform faults or discontinuities' boundary has fundamental implications in our understanding of oceanic accretion, the accommodation of deformation around rigid lithospheric blocks, and the distribution of magmatic and volcanic processes. The now widely used location of mid oceanic ridges worldwide, published by P. Bird in 2003, can be updated based on recent publicly available and published ship-based multibeam swath bathymetry data (100-m resolution or better), now available to ~25% of the ocean seafloor, but covering a significant proportion of the mid-ocean ridge system (>70%). Here we publish the MAPRIDGES database built under the coordination of CGMW (Commission for the Geological Map of the World), with a first version V1.0 (06/2024) that provides high resolution and up-to-date datasets of mid-ocean ridge segments and associated transform faults, and follow-up updates that will also include non-transform offsets. The detailed mapping of individual mid oceanic ridge segments was conducted using GMRT (Ryan et al., 2009) (version 4.2 for MAPRIDGES V1.0), other publicly available datasets (e.g., NCEI, Pangaea, AWI), and existing literature. MAPRIDGES will be revised with the acquisition of additional datasets, new publications, and correction of any errors in the database. The MAPRIDGE database was built in a GIS environment, where each feature holds several attributes specific to the dataset. We include three different georeferenced shapefile layers: 1) Ridge Segments, 2) Transform Faults, and 3) Transform Zones. The latest corresponds to zones of distributed strike-slip deformation that lack a well-defined fault localizing strain, but that are often treated as transform faults. 1) The Ridge Segments Layer contains 1461 segments with 9 attributes: - AREA_LOCA: The Name of the Ridge System - LOC_SHORT: The short form of the Ridge System using 3 characters - LAT: The maximum latitude of the ridge segment - LONG: the maximum longitude of the ridge segment - LENGTH: the length of the ridge segment in meters - CONFIDENCE: the degree of confidence on digitization based on the availability of high-resolution bathymetry data: 1 = low to medium confidence, 2 = high confidence - REFERENCES: supporting references used for the digitization - NAME_CODE: unique segment code constructed from the LOC_SHORT and LAT attributes in degree, minute, second coordinate format - NAME_LIT: name of the segment from the literature if it exists 2) The Transform Fault Layer contains 260 segments with 4 attributes: - NAME_TF: Name of the transform fault according to the literature - LENGTH: length of the transform fault in meters - LAT: The maximum latitude of the fault segment - LONG: the maximum longitude of the fault segment 3) The Transform Zone layer contains 10 segments with 4 attributes: - NAME_TF: Name of the transform zone according to the literature - LENGTH: length of the transform fault in meters - LAT: The maximum latitude of the fault segment - LONG: the maximum longitude of the fault segment To facilitate revisions and updates of the database, relevant information, corrections, or data could be sent to B. Sautter (benjamin.sautter@univ-ubs.fr) and J. Escartín (escartin@geologie.ens.fr).
-
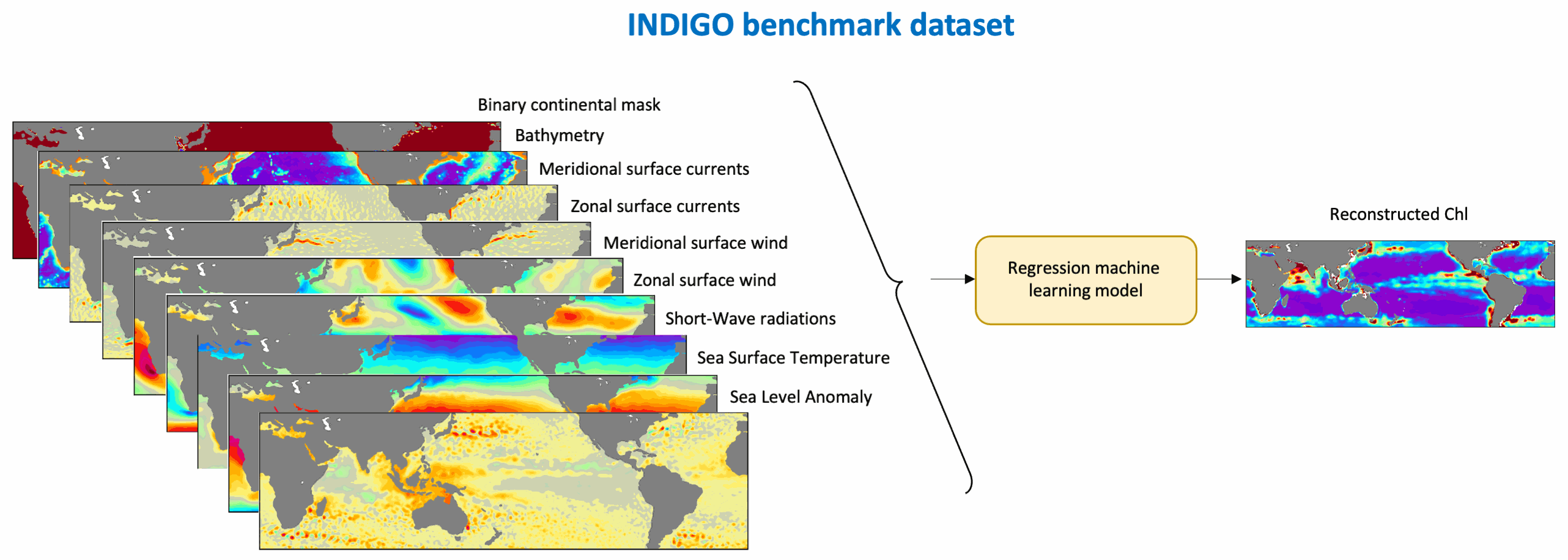
This benchmark dataset contains the physical data used as predictors to reconstruct global chlorophyll-a concentrations (Chl, a proxy of phytoplankton biomass) in Roussillon et al., as well as the reference satellite Chl target fields. The nine physical predictors' data (Short-Wave radiations, Sea Surface Temperature, Sea Level Anomaly, Zonal and meridional surface currents, Zonal and meridional surface wind stress, Bathymetry, Binary continental mask) were extracted from publicly available datasets over [1998-2015] and resampled to the same spatio-temporel resolution as Chl, i.e. monthly on a 1°x1° grid between 50°N and 50°S. Missing values were gap-filled using the heat diffusion equation. Each variable was normalized by substracting its mean from the original values and dividing by its standard deviation over [1998-2015]. This dataset was used to train and validate the Multi-Mode Convolutional Neural network (CNNMM8) introduced in Roussillon et al. ; reconstructed monthly Chl fields over the [2012-2015] test period are also provided here. We hope this benchmark dataset can help to promote the improvements of methods as well as the emergence of new ideas, as building datasets is sometimes more time-consuming than the implementation of machine learning tools themselves. This would also facilitate the quantitative comparison of models performances' on the exact same datasets.
-
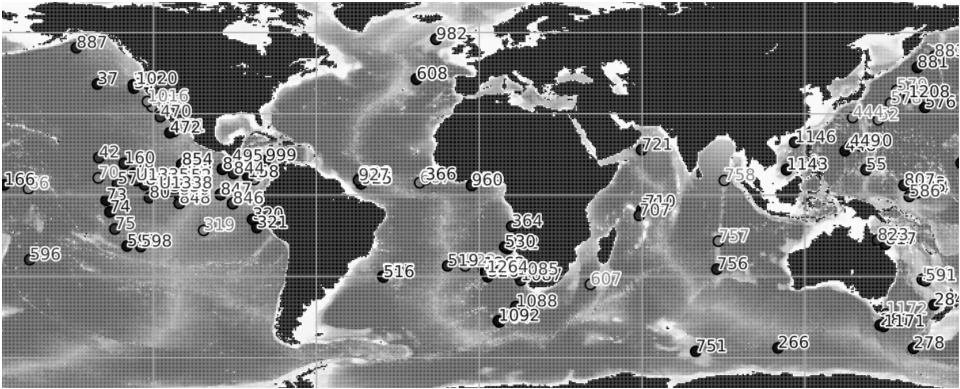
Compilation of published ocean drilling (DSDP, ODP and IODP) records of sedimentation rates, CaCO3, opal and terrigenous accumulation rates that cover the late Miocene and early Pliocene interval. We compiled oceanographic data from DSDP, ODP and IODP expeditions that cover the late Miocene and early Pliocene. Data mining was performed by automatically collecting the Pangaea datasets that correspond to the selected time interval and that have at least one of the following variables: sedimentation rate, dry bulk density, mass accumulation rate (MAR), CaCO3 accumulation rate, bSiO2 accumulation rate (biogenic SiO2) , %CaCO3, %bSiO2. The compilation was then improved by manually adding datasets absent from Pangaea but relevant to our study. The data compilation contains 154 datasets (122 are from Pangaea) from 118 different ocean drilling sites. Age-depth models have been calibrated to the GTS2020 time scale in order to perform a temporal comparison of the datasets. This step was performed using the Neptune Sandbox Berlin database (Renaudie et al. 2020, Palaeontologia Electronica, DOI:10.26879/1032). The Meta_Data_Table file is a metadata table with the following information : site number, dataset label, site label, publication, elevation, site coordinates, site paleocoordinates (10 Ma), available variables, variables used for labeling, the time scale used in the original publication, and the web link to the original dataset. The Time_series file is a file that contains the time series of all the variables in all the data sets in this repository. Each file (.csv) contains a dataset and includes the following information: - Site number - Original link of the dataset - Citation - List of ages - List of values for each variable
-
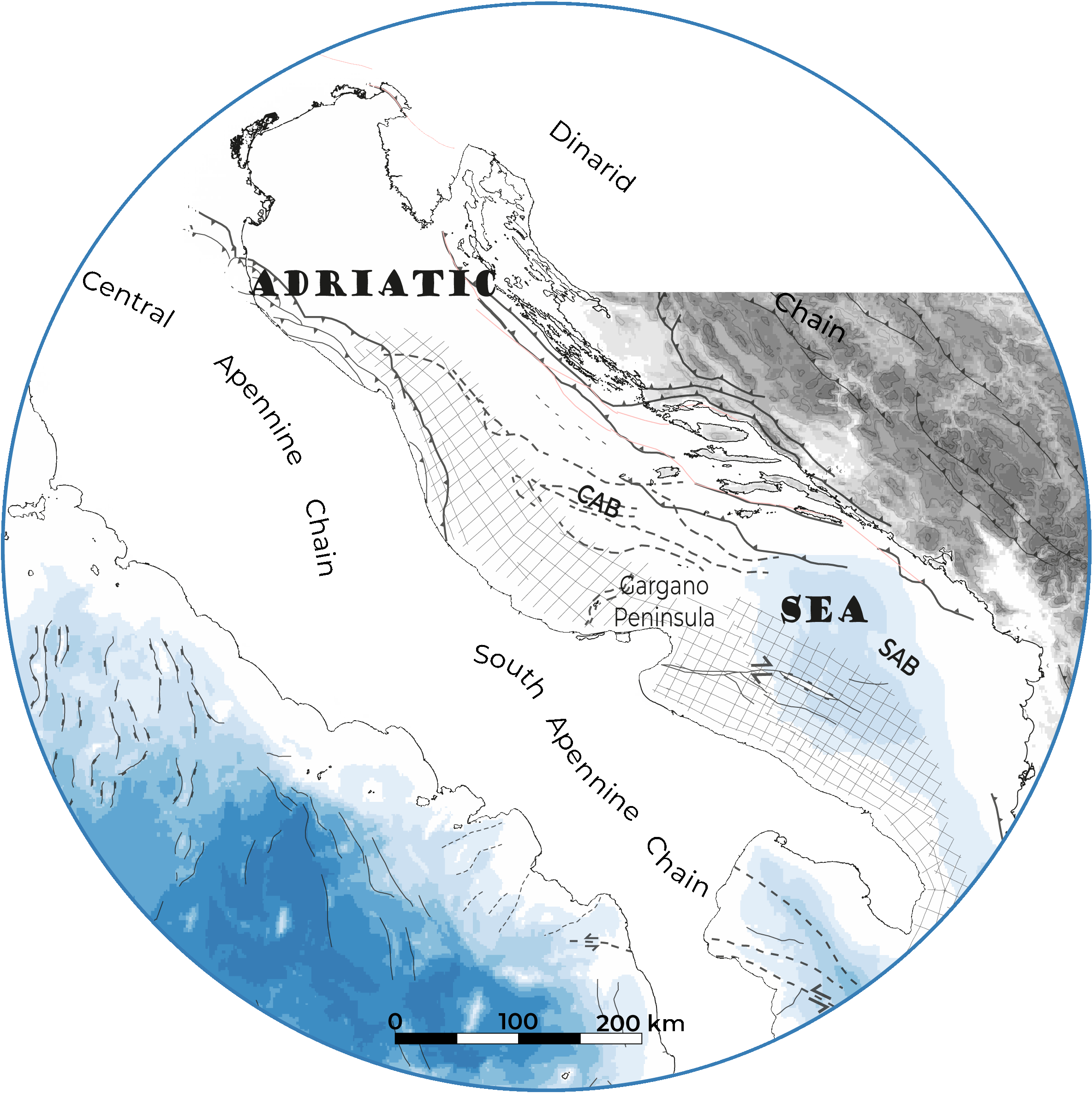
The Mediterranean Sea is a natural laboratory for addressing questions on the formation and evolution of continental margins and the relationship between surface and deep processes. The evaporites deposited during the Messinian Salinity Crisis strongly impact its sedimentary and geomorphology evolution. We present here a compilation of the main regional seismic stratigraphic markers throughout the Central and South Adriatic Sea (CAB and SAB). The following original (uninterpolated) interpretations are provided in xyz format (z in second twt): i) Top of the Mesozoic formation, ii) Base and Top of the Gessoso Solfifera along the CAB, iii) Base and Top of the MSC detrital formation along the SAB, iv) Top of the Upper Unit, v) Base and Top of the middle Pliocene unit, vi) Seafloor. The available reflection seismic dataset the data set is compiled of processed vintage seismic profiles from the Videpi database.
-

The Gambier lagoon has a diamond-shaped form and surrounds seven high islands that are very exposed to the ocean. It is bordered by a barrier reef, which is submerged along the southern and western sides and by an intertidal to emerged barrier reef along the northern and eastern sides. The northern side is cut in some sections by several hoa, (shallow passages) allowing connections between the lagoon and the open ocean. The average depth of the domain is 25 m, with a maximum depth of 80 m along the southeastern coast of Mangareva Island. The bathymetry is complex, forming several basins, including the Rikitea enclosed lagoon, which is bordered by Mangareva and Aukena islands. The bathymetry of the Gambier Islands lagoon was generated using three data sources: SHOM soundings acquired in the 1960s, multi-beam data from Geopolynesie (5 m resolution) collected between 2020 and 2021, and satellite-derived bathymetry (SDB) at 10 m resolution using Sentinel-2 imagery to fill depth gaps in shallow areas. The final bathymetric grid was produced for implementation in the numerical hydrodynamic model MARS3D at a resolution of 100 m, using the compiled sounding datasets described above. The interpolation process included a Hanning low-pass filter applied five consecutive times for depths below 50 m, followed by an additional low-pass filter (ROMS) with a factor of 0.25.
 Metadata catalogue
Metadata catalogue