2011
Type of resources
Available actions
Topics
INSPIRE themes
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
Service types
Scale
Resolution
-
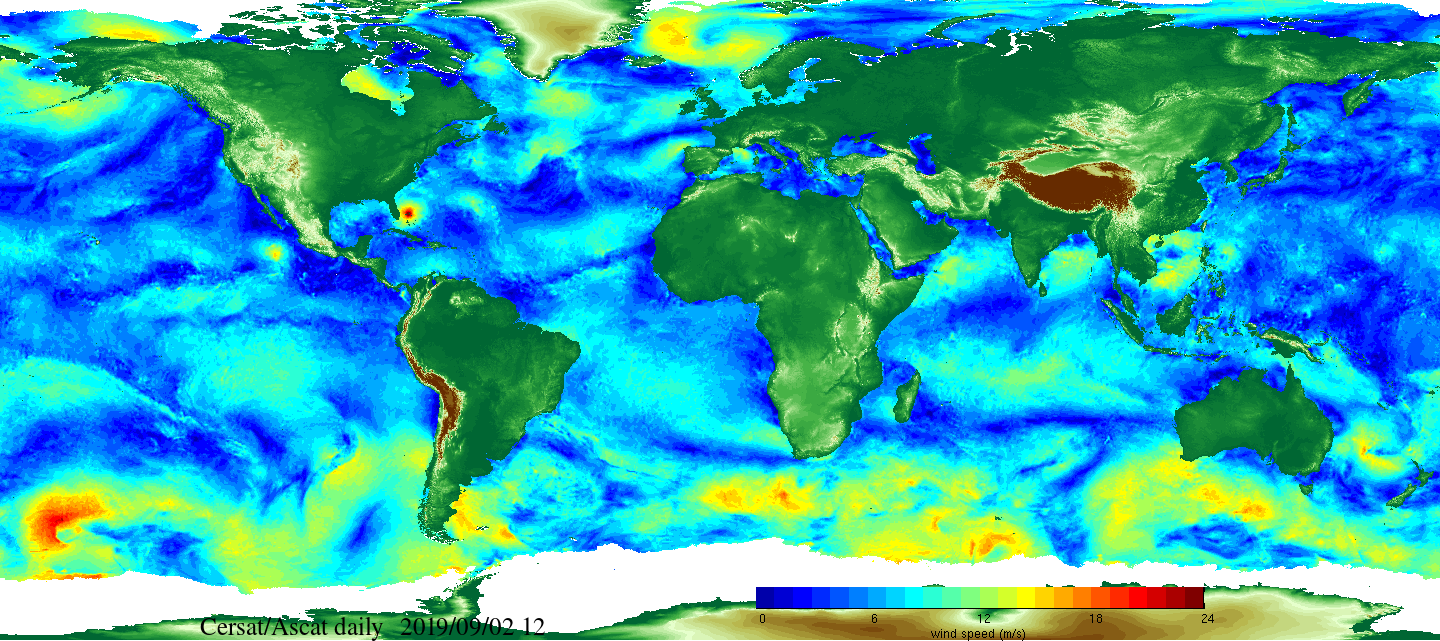
Daily and monthly surface wind analyses are determined as gridded wind products over global oceans, with regular spatial resolution of 0.25° in latitude and longitude. They are estimated from scatterometer wind retrievals (L2b data). According to the scatterometer sampling scheme, the objective method allowing the determination of regular in space surface wind fields uses remotely sensed observations as well as ECMWF analyses. The calculation of daily estimates uses ascending as well as descending available and valid retrievals. The objective method aims to provide daily-averaged gridded wind speed, zonal component, meridional component, wind stress and the corresponding components at global scale. The error associated to each parameter, related to the sampling impact and wind space and time variability, is provided too. Monthly wind analyses are calculated from daily estimates.
-
Data from the British Geological Survey's GeoIndex Map products theme are made available for viewing here. GeoIndex is a website that allows users to search for information about BGS data collections covering the UK and other areas world wide. Access is free, the interface is easy to use, and it has been developed to enable users to check coverage of different types of data and find out some background information about the data. More detailed information can be obtained by further enquiry via the web site: www.bgs.ac.uk/geoindex.
-
The Marine Hard Substrate dataset maps areas of rock or hard substrate outcropping or within 0.5m of the sea-bed. The interpretation was based on a variety of data sourced from within the British Geological Survey and externally. Data consulted includes archive sample and seismic records, side scan sonar, multibeam bathymetry and Olex datasets. The distribution of hard substrate at the seabed, or within 0.5 m is important in dictating the benthic assemblages found in certain areas. Therefore, an understanding of the distribution of these substrates is of primary importance in marine planning and designation of Marine Conservation Zones (MCZs) under the Marine and Coastal Access Act, 2009. In addition, a number of other users will value these data, including marine renewable companies, aggregate companies, the fishing and oil and gas industries. In order to address this issue it was necessary to update British Geological Survey sea-bed mapping to delineate areas where rock, boulders or cobbles are present at, or within 0.5m of the sea-bed surface. A polygon shape file showing areas of rock or hard substrate at, or within 0.5m of the sea-bed has been developed. The dataset has been created as vector polygons and are available in a range of GIS formats, including ArcGIS (.shp), ArcInfo Coverages and MapInfo (.tab). More specialised formats may be available but may incur additional processing costs.
-
Note: This dataset is designed for the 1:50000 scale but can be viewed in this WMS between 1:100000 and 1:25000 (Only). The 1:50 000 DiGMapGB data covering the whole of the United Kingdom is available in this OGC WMS service for your personal, non-commercial use only. Separate bedrock geology, superficial deposits, artificial ground, mass movement deposits and geological linear features layers are available in this service. For information about more of the British Geological Survey's maps that are available digitally please visit http://www.bgs.ac.uk/products/digitalmaps/digmapgb.html.
-
Data from the British Geological Survey's GeoIndex Geochemistry theme are made available for viewing here. GeoIndex is a website that allows users to search for information about BGS data collections covering the UK and other areas world wide. Access is free, the interface is easy to use, and it has been developed to enable users to check coverage of different types of data and find out some background information about the data. More detailed information can be obtained by further enquiry via the web site: www.bgs.ac.uk/geoindex.
-
Data from the British Geological Survey's GeoIndex Geophysics theme are made available for viewing here. GeoIndex is a website that allows users to search for information about BGS data collections covering the UK and other areas world wide. Access is free, the interface is easy to use, and it has been developed to enable users to check coverage of different types of data and find out some background information about the data. More detailed information can be obtained by further enquiry via the web site: www.bgs.ac.uk/geoindex.
-
On 31 January 2011, Part 6 of the Marine (Scotland) Act 2010 came into force. Part 6 seeks to balance seal conservation with sustainable fisheries and aquaculture and its introduction means: It is an offence to kill or injure a seal except under licence or for welfare reasons, outlawing unregulated seal shooting that was permitted under previous legislation A number of seal conservation areas around Scotland will begin to be introduced, designed to protect vulnerable, declining common seal populations A new seal licensing system, providing a well regulated and monitored context for seal management in Scotland has been introduced. Seal Management Areas are: East Coast, Moray Firth, Orkney and North Coast, Shetland, South West Scotland, West Scotland, Western Isles.
-
Data from the British Geological Survey's GeoIndex Hazards theme are made available for viewing here. GeoIndex is a website that allows users to search for information about BGS data collections covering the UK and other areas world wide. Access is free, the interface is easy to use, and it has been developed to enable users to check coverage of different types of data and find out some background information about the data. More detailed information can be obtained by further enquiry via the web site: www.bgs.ac.uk/geoindex.
-
This dataset contains the locations of permanent CCTV cameras in the Edinburgh Council area. The temporary CCTV locations are found on street lights with all-weather power sockets for the CCTV cameras.
-
Data from the British Geological Survey's GeoIndex Boreholes theme are made available for viewing here. GeoIndex is a website that allows users to search for information about BGS data collections covering the UK and other areas world wide. Access is free, the interface is easy to use, and it has been developed to enable users to check coverage of different types of data and find out some background information about the data. More detailed information can be obtained by further enquiry via the web site: www.bgs.ac.uk/geoindex.
 Metadata catalogue
Metadata catalogue