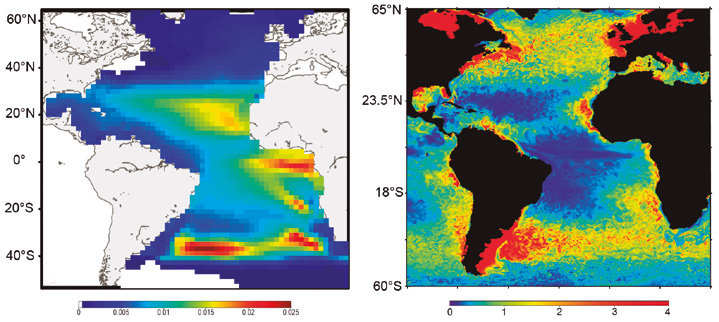
Spatial Ecosystem And POpulation DYnamics Model (SEAPODYM)
SEAPODYM has been initiated in the mid-1990s by the Oceanic Fisheries Programme of the Secretariat of the Pacific Community (SPC) and developed under several European development projects. The objective was to propose new management tools taking into account both the fishing impact and environmental variability.
Since 2006, in partnership with SPC, its development has continued with the Marine Ecosystem Modeling team of CLS (Collecte Localisation Satellite). CLS aims to combine this modeling approach with satellite observation and real-time data collection to develop operational real-time applications and advise government administrations on the sustainable management and monitoring of marine resources.
The main features of SEAPODYM framework are:
- Prediction of the temporal and spatial distributions of functional lower and mid-trophic level groups (Lehodey et al. 2010; 2015)
- Prediction of the temporal and spatial distributions of age-structured predator (fish) populations (Lehodey et al. 2008);
- Prediction of the total catch and the size-frequency of catch by fishing fleet;
- Parameter optimization based on data assimilation techniques (Senina et al., 2008);
The lower and mid-trophic level (LMTL) sub-model describes the dynamics of a functional group of zooplankton and several vertically migrant and non-migrant micronekton (prey of larger fish) groups. The dynamics are linked to temperature and currents. Assimilation of acoustic or biomass data is used to estimate the model parameters.
The dynamics of fish populations are estimated using habitat indices, movements, growth and mortality.
The feeding habitat is based on the accessibility of fish to the groups of prey.
The spawning habitat combines temperature preference and coincidence of spawning with presence or absence of predators and food for larvae. Successful larval recruitment is linked to spawning stock biomass and mortality during the drift with currents.
Older fish can swim along the gradient of habitat index in addition to being advected by ocean currents.
|
|
Citation proposal
. Spatial Ecosystem And POpulation DYnamics Model (SEAPODYM). https://services.mspdata.eu:/geonetwork/srv/api/records/96d5febc-df92-4c52-b087-c13ff86fa668 |
Simple
- Date ( Creation )
- 1995-01-01
- Identifier
- 96d5febc-df92-4c52-b087-c13ff86fa668
- Credit
- Collecte Localisation Satellites (CLS)
- Credit
- Pacific Community (SPC)
Point of contact
- Thèmes Sextant ( Theme )
-
- GEMET - INSPIRE themes, version 1.0 ( Theme )
-
- Mission Atlantic - Resources ( Theme )
-
- Tool
- Mission Atlantic - Work Package ( Theme )
-
- WP6 Dynamics of ecosystem state and resources
- Access constraints
- Copyright
- Use constraints
- Copyright
- Metadata language
- English
- Character set
- UTF8
- Topic category
-
- Oceans
Spatial representation info
- OnLine resource
- SEAPODYM website
- Hierarchy level
- Software
Metadata
- File identifier
- 96d5febc-df92-4c52-b087-c13ff86fa668 XML
- Metadata language
- English
- Character set
- UTF8
- Hierarchy level
- Software
- Date stamp
- 2021-12-08T14:35:37
- Metadata standard name
- ISO 19115:2003/19139 - SEXTANT
- Metadata standard version
- 1.0
Point of contact
- Website
- https://sextant.ifremer.fr/eng
 Metadata catalogue
Metadata catalogue